Kubernetes集群搭建:基于Kubeadm
閱讀本文約花費: 16 (分鐘)
一,环境准备
* K8S版本为15.1
* Docker版本最高支持18.06.1
二,Docker环境构建及替换
1,清除原Docker环境,原版本为最新版
| yum remove docker \ docker-client \ docker-client-latest \ docker-common \ docker-latest \ docker-latest-logrotate \ docker-logrotate \ docker-selinux \ docker-engine-selinux \ docker-engine rm -rf /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d rm -rf /var/lib/docker rm -rf /var/run/docker |
2,如果清除后依旧包冲突错误
| file /usr/share/man/man1/docker-manifest-annotate.1.gz from install of docker-ce-18.06.1.ce-3.el7.x86_64 conflicts with file from package docker-ce-cli-1:18.09.6-3.el7.x86_64 |
通过yum命令手动移除冲突包
| yum erase docker-common-2:1.12.6-68.gitec8512b.el7.centos.x86_64 |
3,安装18.06.1版本Docker
| yum install -y docker-ce-18.06.1.ce-3.el7 |
三,Kubernetes集群环境搭建
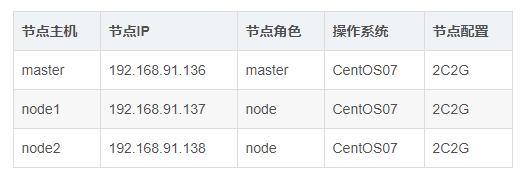
1,基础环境准备
a,机器节点准备,虚拟机搭建,内存不够,host名称只支持[-.]两个特殊符号
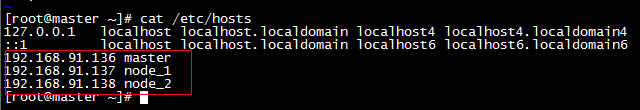
b,/etc/hosts文件设置
* 添加命令
| cat >> /etc/hosts << EOF 192.168.91.136 master 192.168.91.137 node1 192.168.91.138 node2 EOF |
* hosts文件配置如下
c,配置时间同步,使用chrony同步时间,配置master节点与网络NTP服务器同步时间,所有node节点与master节点同步时间
* 配置Master节点
| // 安装chrony: yum install -y chrony // 注释默认ntp服务器 sed -i ‘s/^server/#&/’ /etc/chrony.conf // 指定上游公共 ntp 服务器,并允许其他节点同步时间 cat >> /etc/chrony.conf << EOF server 0.asia.pool.ntp.org iburst server 1.asia.pool.ntp.org iburst server 2.asia.pool.ntp.org iburst server 3.asia.pool.ntp.org iburst allow all EOF // 重启chronyd服务并设为开机启动: systemctl enable chronyd && systemctl restart chronyd // 开启网络时间同步功能 timedatectl set-ntp true |
* 配置Node节点
| // 安装chrony: yum install -y chrony // 注释默认服务器 sed -i ‘s/^server/#&/’ /etc/chrony.conf // 指定内网 master节点为上游NTP服务器 echo server 192.168.91.128 iburst >> /etc/chrony.conf // 重启服务并设为开机启动: systemctl enable chronyd && systemctl restart chronyd |
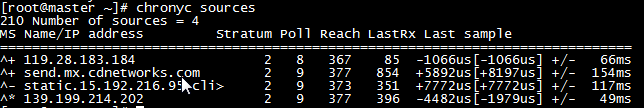
*所有节点执行chronyc sources命令,查看存在以^*开头的行,说明已经与服务器时间同步
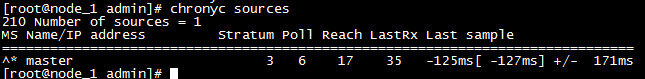
d,设置网桥包经过iptalbes?RHEL / CentOS 7上的一些用户报告了由于iptables被绕过而导致流量路由不正确的问题。创建/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf文件,添加如下内容
| // 添加文件内容 cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf vm.swappiness = 0 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 EOF // 使配置生效 modprobe br_netfilter sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf |
e,kube-proxy开启ipvs的前提条件?由于ipvs已经加入到了内核的主干,所以为kube-proxy开启ipvs的前提需要加载以下的内核模块: 在所有的Kubernetes节点执行以下脚本
| // 添加内容 cat > /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules <<EOF #!/bin/bash modprobe — ip_vs modprobe — ip_vs_rr modprobe — ip_vs_wrr modprobe — ip_vs_sh modprobe — nf_conntrack_ipv4 EOF // 执行脚本 chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules && bash /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules && lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4 |
f,上面脚本创建了/etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules文件,保证在节点重启后能自动加载所需模块。 使用lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4命令查看是否已经正确加载所需的内核模块。 接下来还需要确保各个节点上已经安装了ipset软件包。 为了便于查看ipvs的代理规则,最好安装一下管理工具ipvsadm。
| yum install ipset ipvsadm -y |
g,安装kubeadm、kubelet、kubectl
| // 配置kubernetes.repo的源, 由于官方源国内无法访问,这里使用阿里云yum源 cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com /kubernetes/yum /repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com /kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com /kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF // 在所有节点上安装指定版本 kubelet、kubeadm 和 kubectl // 此处直接下载版本为1.15.1 yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl // 启动kubelet服务 systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet |
2,Master环境搭建
a,安装废了后,重置节点
| kubeadm reset |
b,初始化Master节点,注意对address和version进行更改,version与kubeadm等版本一致
| kubeadm init \ –apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.91.136 \ –image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers \ –kubernetes-version v1.15.1 \ –pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 |
*apiserver-advertise-address:指明用 Master 的哪个 interface 与 Cluster 的其他节点通信。如果 Master 有多个 interface,建议明确指定,如果不指定,kubeadm 会自动选择有默认网关的 interface。
*pod-network-cidr:指定 Pod 网络的范围。Kubernetes 支持多种网络方案,而且不同网络方案对 –pod-network-cidr 有自己的要求,这里设置为 10.244.0.0/16 是因为我们将使用 flannel 网络方案,必须设置成这个 CIDR。
*image-repository:Kubenetes默认Registries地址是?k8s.gcr.io,在国内并不能访问gcr.io,在1.15版本中我们可以增加–image-repository参数,默认值是k8s.gcr.io,将其指定为阿里云镜像地址:registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers。
*kubernetes-version=v1.15.1:关闭版本探测,因为它的默认值是stable-1,会导致从https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable-1.txt下载最新的版本号,我们可以将其指定为固定版本(最新版:v1.13.1)来跳过网络请求。
c,初始化过程,及说明
| [root@master ~]# kubeadm init –apiserver-advertise-address=192.168.91.136 –image-repository registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers –kubernetes-version v1.15.1 –pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 [init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.15.1 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [WARNING IsDockerSystemdCheck]: detected “cgroupfs” as the Docker cgroup driver. The recommended driver is “systemd”. Please follow the guide at https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/cri/ [preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster [preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection [preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using ‘kubeadm config images pull’ [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file “/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env” [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file “/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml” [kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service [certs] Using certificateDir folder “/etc/kubernetes/pki” [certs] Generating “front-proxy-ca” certificate and key [certs] Generating “front-proxy-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “etcd/ca” certificate and key [certs] Generating “etcd/server” certificate and key [certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [master localhost] and IPs [192.168.91.136 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating “etcd/peer” certificate and key [certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [master localhost] and IPs [192.168.91.136 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating “etcd/healthcheck-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “apiserver-etcd-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “ca” certificate and key [certs] Generating “apiserver-kubelet-client” certificate and key [certs] Generating “apiserver” certificate and key [certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [master kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 192.168.91.136] [certs] Generating “sa” key and public key [kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder “/etc/kubernetes” [kubeconfig] Writing “admin.conf” kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing “kubelet.conf” kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing “controller-manager.conf” kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing “scheduler.conf” kubeconfig file [control-plane] Using manifest folder “/etc/kubernetes/manifests” [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for “kube-apiserver” [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for “kube-controller-manager” [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for “kube-scheduler” [etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in “/etc/kubernetes/manifests” [wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory “/etc/kubernetes/manifests”. This can take up to 4m0s [apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 25.517374 seconds [upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap “kubeadm-config” in the “kube-system” Namespace [kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap “kubelet-config-1.15” in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster [upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see –upload-certs [mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the label “node-role.kubernetes.io/master=”” [mark-control-plane] Marking the node master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule] [bootstrap-token] Using token: qozff5.j2weqyh2uhcz4l7f [bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster [bootstrap-token] Creating the “cluster-info” ConfigMap in the “kube-public” namespace [addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS [addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run “kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml” with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join 192.168.91.136:6443 –token qozff5.j2weqyh2uhcz4l7f \ –discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f427679e26a28dec67 138e2806c4ec2c03827665dd1233b11e7f60cb3c260b60 |
*[preflight] kubeadm 执行初始化前的检查
*[kubelet-start] 生成kubelet的配置文件”/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml”
*[certificates] 生成相关的各种token和证书
*[certificates] 生成相关的各种token和证书
*[kubeconfig] 生成 KubeConfig 文件,kubelet 需要这个文件与 Master 通信
*[control-plane] 安装 Master 组件,会从指定的 Registry 下载组件的 Docker 镜像。
*[bootstraptoken] 生成token记录下来,后边使用kubeadm join往集群中添加节点时会用到
*[addons] 安装附加组件 kube-proxy 和 kube-dns。
*Kubernetes Master 初始化成功,提示如何配置常规用户使用kubectl访问集群。
*提示如何安装 Pod 网络。
*提示如何注册其他节点到 Cluster。
* join命令必须记住,后续需要使用join对应的token添加node节点
d,配置 kubectl:kubectl 是管理 Kubernetes Cluster 的命令行工具,前面我们已经在所有的节点安装了 kubectl。Master 初始化完成后需要做一些配置工作,然后 kubectl 就能使用了。需要这些配置命令的原因是:Kubernetes 集群默认需要加密方式访问。所以,这几条命令,就是将刚刚部署生成的 Kubernetes 集群的安全配置文件,保存到当前用户的.kube 目录下,kubectl 默认会使用这个目录下的授权信息访问 Kubernetes 集群。 如果不这么做的话,我们每次都需要通过 export KUBECONFIG 环境变量告诉 kubectl 这个安全配置文件的位置。 配置完成后centos用户就可以使用 kubectl 命令管理集群了。(此演示直接在root账号运行)
| // 追加sudo权限,并配置sudo免密 sed -i ‘/^root/a\centos ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL’ /etc/sudoers // 保存集群安全配置文件到当前用户.kube目录 mkdir -p $HOME/.kube cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config // 启用 kubectl 命令自动补全功能(注销重新登录生效) echo “source <(kubectl completion bash)” >> ~/.bashrc |
e,配置好Master节点后,查看集群状态,确定每一个组件都处于healthy状态
| kubectl get cs |
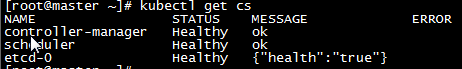
f,确定组件都处于healthy状态后,查看节点状态
| kubectl get nodes |
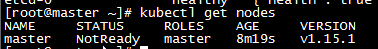
g,只有一个Master节点,且节点处于NotReady状态。使用 kubectl describe 命令来查看这个节点(Node)对象的详细信息、状态和事件(Event)
| kubectl describe node master |
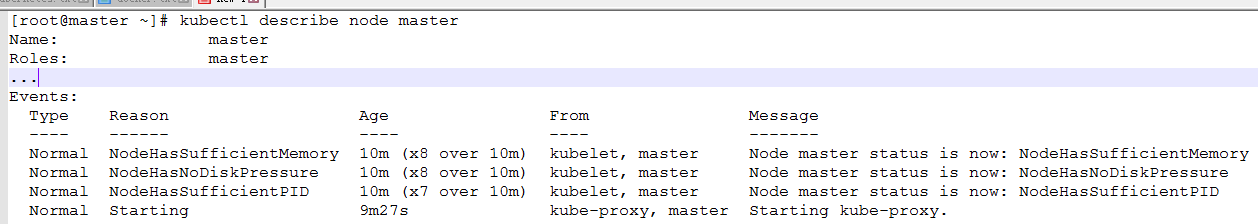
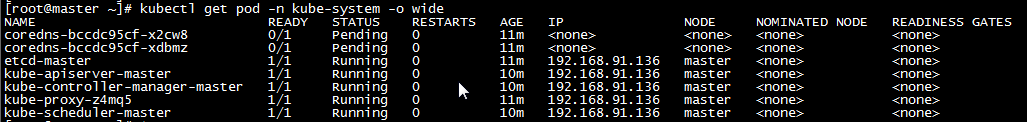
h,通过 kubectl describe 指令的输出,我们可以看到 NodeNotReady 的原因在于,我们尚未部署任何网络插件,kube-proxy等组件还处于starting状态。 另外,我们还可以通过 kubectl 检查这个节点上各个系统 Pod 的状态,其中,kube-system 是 Kubernetes 项目预留的系统 Pod 的工作空间(Namepsace,注意它并不是 Linux Namespace,它只是 Kubernetes 划分不同工作空间的单位),可以看到,CoreDNS依赖于网络的 Pod 都处于 Pending 状态,即调度失败。这当然是符合预期的:因为这个 Master 节点的网络尚未就绪
| kubectl get pod -n kube-system -o wide |
i,部署网络插件?要让 Kubernetes Cluster 能够工作,必须安装 Pod 网络,否则 Pod 之间无法通信。 Kubernetes 支持多种网络方案,这里我们使用 flannel 执行如下命令部署 flannel: kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
* 上传 kube-flannel.yml 文件,文件内容如下
| — kind: ClusterRole apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: flannel rules: – apiGroups: – “” resources: – pods verbs: – get – apiGroups: – “” resources: – nodes verbs: – list – watch – apiGroups: – “” resources: – nodes/status verbs: – patch — kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: flannel roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: flannel subjects: – kind: ServiceAccount name: flannel namespace: kube-system — apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: flannel namespace: kube-system — kind: ConfigMap apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: kube-flannel-cfg namespace: kube-system labels: tier: node app: flannel data: cni-conf.json: | { “name”: “cbr0”, “plugins”: [ { “type”: “flannel”, “delegate”: { “hairpinMode”: true, “isDefaultGateway”: true } }, { “type”: “portmap”, “capabilities”: { “portMappings”: true } } ] } net-conf.json: | { “Network”: “10.244.0.0/16”, “Backend”: { “Type”: “vxlan” } } — apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: kube-flannel-ds-amd64 namespace: kube-system labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: template: metadata: labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: hostNetwork: true nodeSelector: beta.kubernetes.io/arch: amd64 tolerations: – operator: Exists effect: NoSchedule serviceAccountName: flannel initContainers: – name: install-cni image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-amd64 command: – cp args: – -f – /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json – /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist volumeMounts: – name: cni mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ containers: – name: kube-flannel image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-amd64 command: – /opt/bin/flanneld args: – –ip-masq – –kube-subnet-mgr resources: requests: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” limits: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” securityContext: privileged: true env: – name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name – name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace volumeMounts: – name: run mountPath: /run – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ volumes: – name: run hostPath: path: /run – name: cni hostPath: path: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg configMap: name: kube-flannel-cfg — apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: kube-flannel-ds-arm64 namespace: kube-system labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: template: metadata: labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: hostNetwork: true nodeSelector: beta.kubernetes.io/arch: arm64 tolerations: – operator: Exists effect: NoSchedule serviceAccountName: flannel initContainers: – name: install-cni image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-arm64 command: – cp args: – -f – /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json – /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist volumeMounts: – name: cni mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ containers: – name: kube-flannel image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-arm64 command: – /opt/bin/flanneld args: – –ip-masq – –kube-subnet-mgr resources: requests: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” limits: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” securityContext: privileged: true env: – name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name – name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace volumeMounts: – name: run mountPath: /run – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ volumes: – name: run hostPath: path: /run – name: cni hostPath: path: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg configMap: name: kube-flannel-cfg — apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: kube-flannel-ds-arm namespace: kube-system labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: template: metadata: labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: hostNetwork: true nodeSelector: beta.kubernetes.io/arch: arm tolerations: – operator: Exists effect: NoSchedule serviceAccountName: flannel initContainers: – name: install-cni image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-arm command: – cp args: – -f – /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json – /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist volumeMounts: – name: cni mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ containers: – name: kube-flannel image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-arm command: – /opt/bin/flanneld args: – –ip-masq – –kube-subnet-mgr resources: requests: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” limits: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” securityContext: privileged: true env: – name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name – name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace volumeMounts: – name: run mountPath: /run – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ volumes: – name: run hostPath: path: /run – name: cni hostPath: path: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg configMap: name: kube-flannel-cfg — apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: kube-flannel-ds-ppc64le namespace: kube-system labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: template: metadata: labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: hostNetwork: true nodeSelector: beta.kubernetes.io/arch: ppc64le tolerations: – operator: Exists effect: NoSchedule serviceAccountName: flannel initContainers: – name: install-cni image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-ppc64le command: – cp args: – -f – /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json – /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist volumeMounts: – name: cni mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ containers: – name: kube-flannel image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-ppc64le command: – /opt/bin/flanneld args: – –ip-masq – –kube-subnet-mgr resources: requests: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” limits: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” securityContext: privileged: true env: – name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name – name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace volumeMounts: – name: run mountPath: /run – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ volumes: – name: run hostPath: path: /run – name: cni hostPath: path: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg configMap: name: kube-flannel-cfg — apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: DaemonSet metadata: name: kube-flannel-ds-s390x namespace: kube-system labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: template: metadata: labels: tier: node app: flannel spec: hostNetwork: true nodeSelector: beta.kubernetes.io/arch: s390x tolerations: – operator: Exists effect: NoSchedule serviceAccountName: flannel initContainers: – name: install-cni image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-s390x command: – cp args: – -f – /etc/kube-flannel/cni-conf.json – /etc/cni/net.d/10-flannel.conflist volumeMounts: – name: cni mountPath: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ containers: – name: kube-flannel image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-s390x command: – /opt/bin/flanneld args: – –ip-masq – –kube-subnet-mgr resources: requests: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” limits: cpu: “100m” memory: “50Mi” securityContext: privileged: true env: – name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name – name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace volumeMounts: – name: run mountPath: /run – name: flannel-cfg mountPath: /etc/kube-flannel/ volumes: – name: run hostPath: path: /run – name: cni hostPath: path: /etc/cni/net.d – name: flannel-cfg configMap: name: kube-flannel-cfg |
* 执行文件
| kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml |
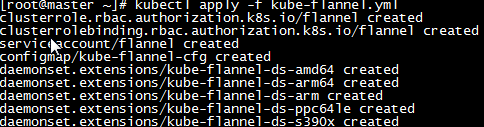
j,安装成功flannel网络插件后,重新查看POD状态。圈出来的部分,可能会存在短暂的init状态,稍等即可
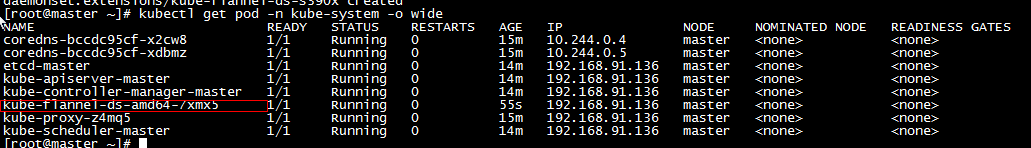
*pod状态为Pending、ContainerCreating、ImagePullBackOff 都表明 Pod 没有就绪,Running 才是就绪状态,如果pod状态异常,可以通过命令拉取异常信息
| // kube-flannel-ds-amd64-d2r8p 表示pod名称 kubectl describe pod kube-flannel-ds-amd64-d2r8p –namespace=kube-system |
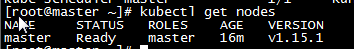
k,重新查看节点状态,节点状态从notReady转为ready,Master节点部署完成,在默认情况下,Kubernetes 的 Master 节点是不能运行用户 Pod 的。
3,Worker环境搭建
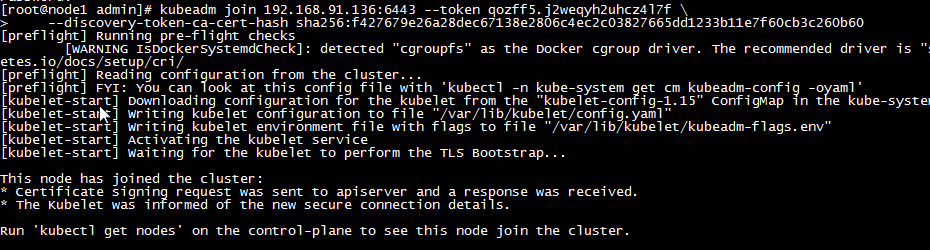
a,执行init时候提示的join语句,显示下列信息说明添加成功
| kubeadm join 192.168.91.136:6443 –token qozff5. j2weqyh2uhcz4l7f \ –discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f427679e26a28dec67138 e2806c4ec2c03827665dd1233b11e7f60cb3c260b60 |
b,如果忘了记住join信息,可以通过语句重新生成
| kubeadm token create –print-join-command |
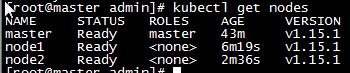
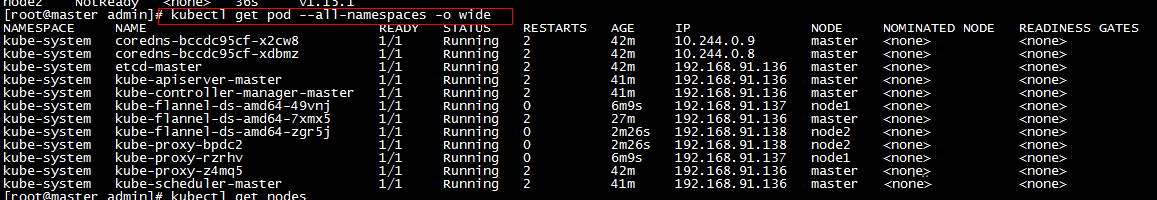
c,重复上一步添加node2节点,添加后,在master节点查看节点及pod。如果存在NotReady节点,可以稍等会,等pod全部启动,或者查看pod状态,对不是Running状态的pod进行具体分析!(pod状态为Pending、ContainerCreating、ImagePullBackOff 都表明 Pod 没有就绪)
d,集群至此,全部搭建完成
四,集群验证
1,首先验证kube-apiserver, kube-controller-manager, kube-scheduler, pod network 是否正常:?部署一个 Nginx Deployment,包含2个Pod?
a,创建
| // 创建deployment nginx [root@master admin]# kubectl create deployment nginx –image=nginx:alpine deployment.apps/nginx created // 设置为两个副本 [root@master admin]# kubectl scale deployment nginx –replicas=2 deployment.extensions/nginx scaled |
b,查看
| [root@master admin]# kubectl get pods -l app=nginx -o wide |

2,再验证一下kube-proxy是否正常:以 NodePort 方式对外提供服务
| // 以NodePort运行,并开放80端口 [root@master admin]# kubectl expose deployment nginx –port=80 –type=NodePort service/nginx exposed // 查看详情 [root@master admin]# kubectl get services nginx NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE nginx NodePort 10.98.47.23 <none> 80:30018/TCP 5s |